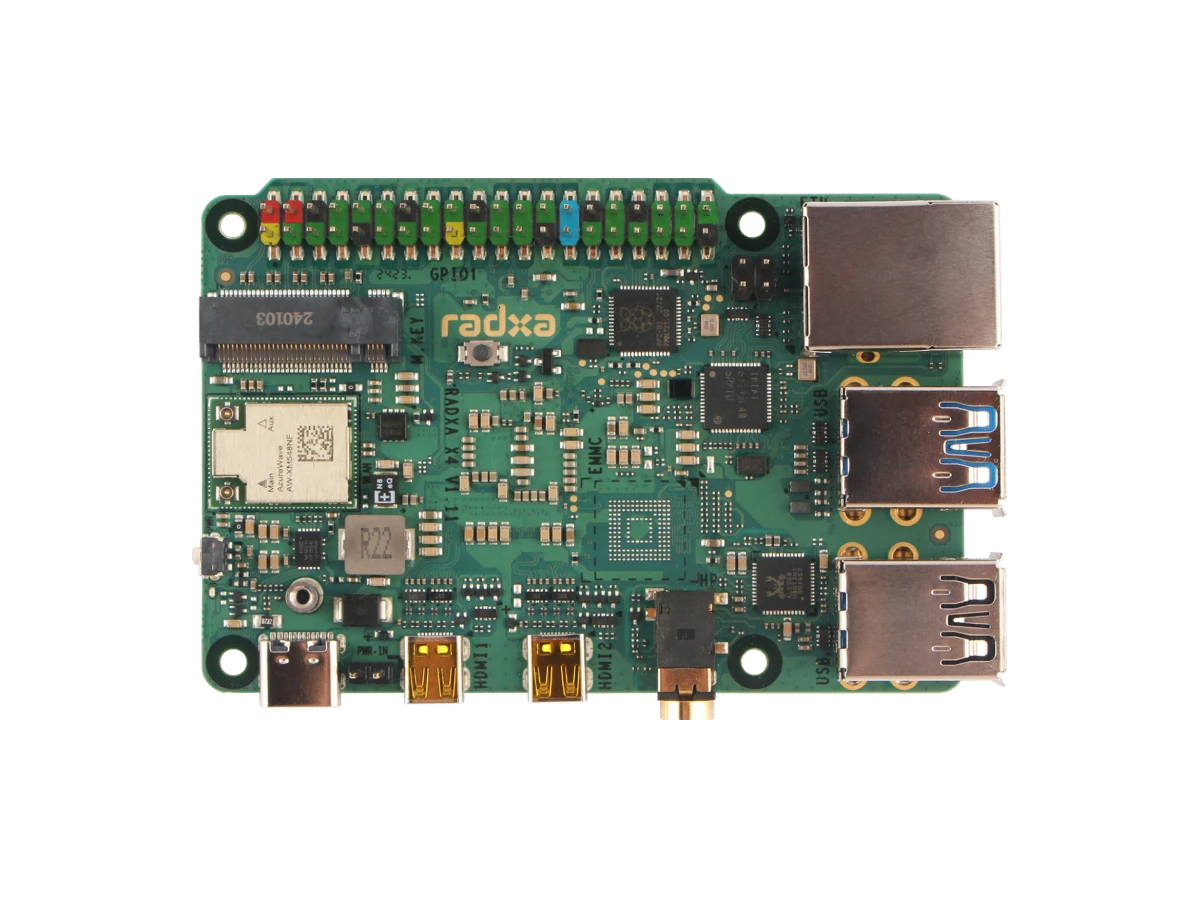
Radxa X4 The Game Changer in SBC Computing – For years, the Raspberry Pi has been the gold standard for SBCs (Single Board Computers). It’s widely adopted for IoT, small home projects, NAS setups, and personal web servers. The Raspberry Pi 5 (RPi5) continues this tradition, offering a decent upgrade in processing power, connectivity, and efficiency for lightweight computing. However, when it comes to serious desktop-tier computing, software compatibility, and scalability, ARM-based SBCs still have inherent limitations.
Enter the Radxa X4, an Intel N100-powered x86 SBC that disrupts the landscape, turning SBCs into legitimate heavy-duty solutions for advanced computing, NAS deployments, media centers, and professional embedded applications.


Why the Radxa X4 is a Game Changer
1. x86 Architecture: Full Desktop-Grade Computing
One of the biggest bottlenecks of ARM-based SBCs like the Raspberry pi 5 is software compatibility. Many software packages, drivers, and enterprise tools are still primarily developed for x86. With the Radxa X4’s Intel N100 processor, users get:
- Native Windows & Linux support without the need for ARM-specific builds or workarounds.
- Full-fledged virtualization capabilities for Docker, VMs, and containerized applications.
- Superior driver support for peripherals, as x86 has decades of legacy support that ARM lacks.
Additionally, the Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller onboard ensures GPIO functionality, supporting C/C++, MicroPython, and IDEs like VS Code & Arduino IDE.
This makes the Radxa X4 a true desktop-class SBC, suitable for workloads that would be unthinkable on an Raspberry pi 5.
2. Built-in NVMe SSD Support: A Storage Revolution
Unlike the Raspberry pi 5, which lacks native NVMe support, the Radxa X4 includes an M.2 M-Key slot. This is a game-changer for performance and reliability, allowing users to:
- Direct Gen 3.0 NVMe booting—no need for external USB adapters.
- Higher read/write speeds—far beyond microSD cards or eMMC.
- Increased reliability—NVMe drives last longer than microSD cards, especially under high I/O workloads.
For serious SBC users looking for storage efficiency, this removes a critical bottleneck that the Raspberry Pi 5 still suffers from out-of-the-box. For power users running databases, VMs, or NAS applications, the Radxa X4’s native Gen 3.0 NVMe support is a game-changer.
3. Robust Storage with Built-in eMMC
The Radxa X4 also comes with optional built-in eMMC storage (up to 128GB). eMMC is significantly more reliable than microSD cards, especially for operating systems and frequently accessed data for those looking to keep costs friendly.
- eMMC is more reliable—microSD cards are prone to corruption and wear out faster.
- Cost-efficiency—entry-level NVMe and eMMC storage is cheaper and faster than endurance-class microSD cards.
- Plug-and-play usability—no need for external boot drives if eMMC is included at purchase.
For users seeking stability, Radxa’s built-in eMMC and NVMe options eliminate the Raspberry Pi’s biggest storage bottleneck.
4. Memory Configurations: More RAM, More Possibilities
While the Raspberry Pi 5 offers up to 16GB of RAM in 2025, the Radxa X4 offers more more flexibility to utilize the full 16GB buffer unlike the raspberry pi 5 due to its faster N100 processing power:
- The Radxa X4 comes in — 4GB, 8GB, 12GB, and even 16GB LPDDR5 options.
- Ideal for heavier workloads — like running full desktop environments, databases, or AI applications.
- More RAM and CPU grunt — improves performance for Docker, virtualization, and high-memory applications.
This gives users the freedom to scale their SBC computing needs without hitting a hardware limitation too soon. Check out the comprehensive analysis I did to evaluate the efficacy of the real-world use cases for the Raspberry Pi 5 16GB Variant and which system you should consider based on your use case.
Fine-Tuning for Maximum Performance
While the Radxa X4 is powerful out-of-the-box, there are essential optimizations required to unlock its full potential.
1. BIOS Tuning: Unlocking the Full Power of the Intel N100
One key limitation found in early BIOS versions is the locked turbo multiplier at 29x, capping the CPU at 2.9 GHz. However:
- Update BIOS to unlock the 34x multiplier (from 29x)
- Adjust power envelope to 12W for peak performance
- Requires proper cooling modifications to sustain performance
- 🔗 BIOS Download: Radxa Official BIOS Release
For users willing to tinker, these adjustments significantly boost the SBC’s processing power, making it a true desktop-class SBC.
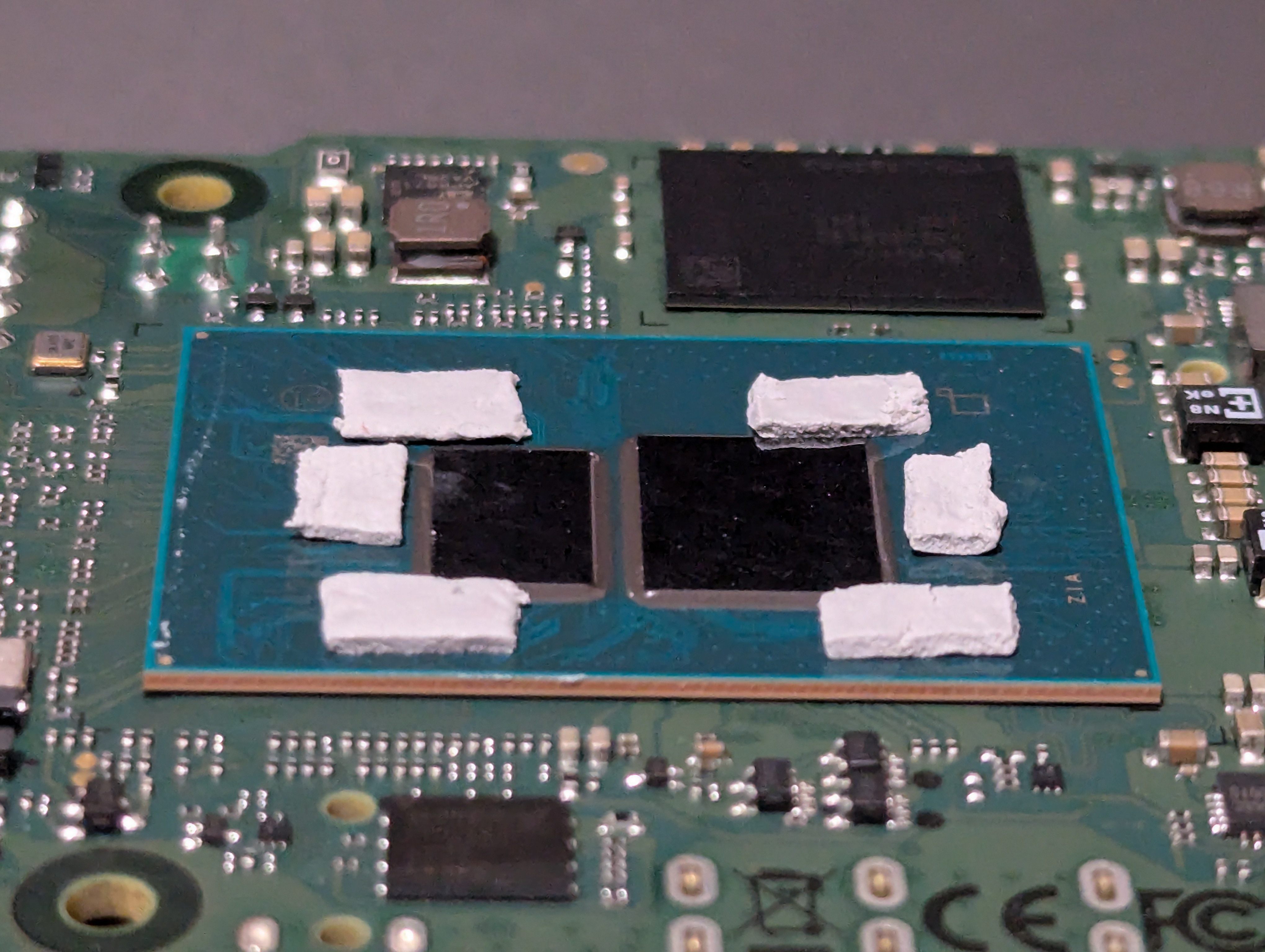
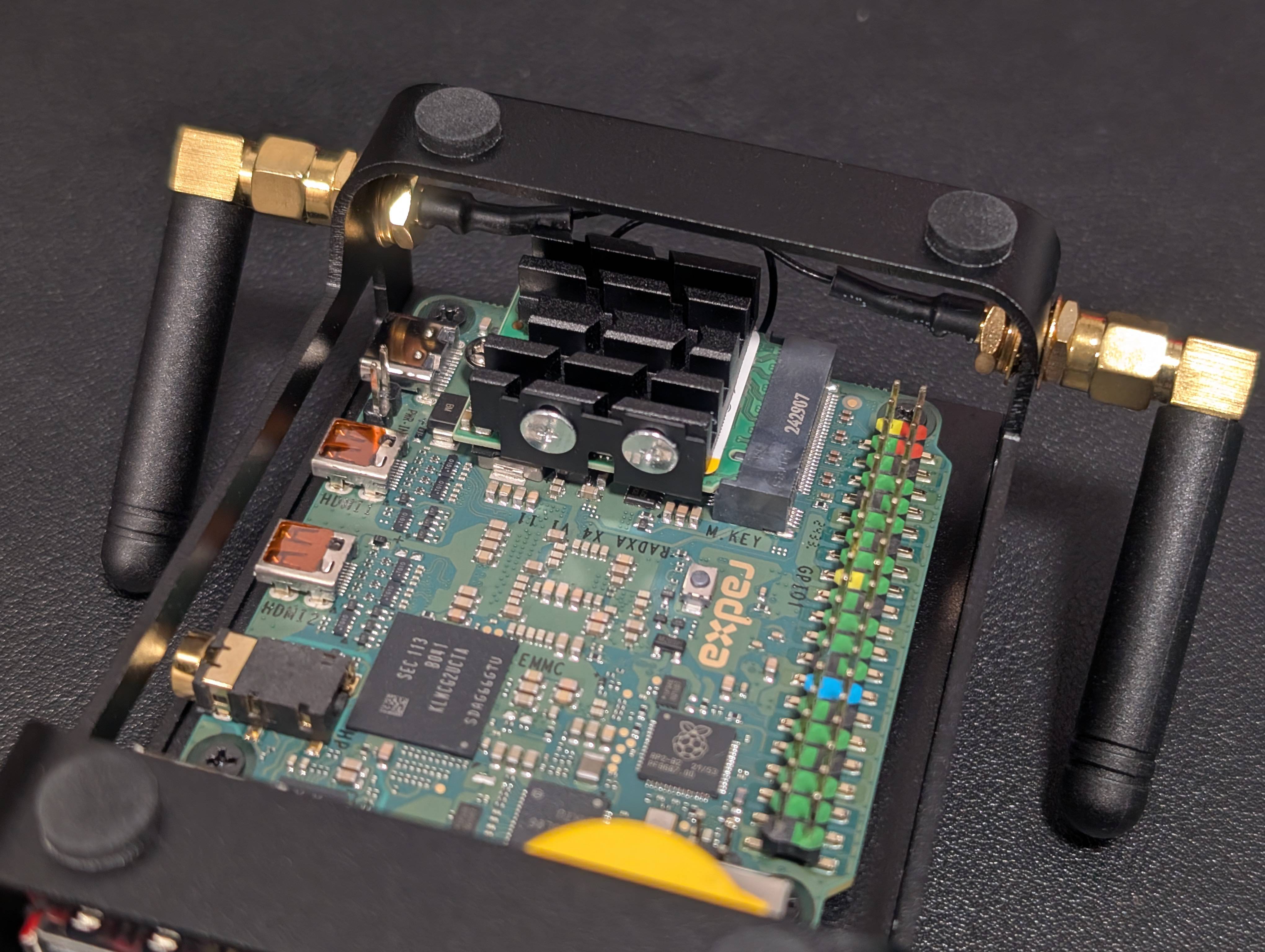
2. Thermal Management: The Copper Shim Mod
For those looking to push the Radxa X4 to its absolute limits, especially when running the Intel N100 at a 15W power envelope to unlock the full 34x multiplier, effective cooling is critical. Out of the box, the Radxa X4’s stock aluminum heatsink does an acceptable job with its stock 6w thermal envelope, but for sustained performance under heavier workloads, thermal optimization is necessary.
Youtube channel ExplainingComputers did an excellent review and covered the use of the copper-shim and its improvements here (16:29).
- Without proper cooling, performance drops due to thermal throttling.
- With a copper shim mod, users have reported sustained turbo clocks of 3.4 GHz.
- The recommended shim thickness is 1mm while thermal pads should be 2mm for surrounding components if desired (Memory, Power management mosfets, etc).
This means that while the Radxa X4 is a powerhouse, it does require additional cooling modifications to extract maximum performance—a small price to pay for an x86 powerhouse in an SBC form factor.
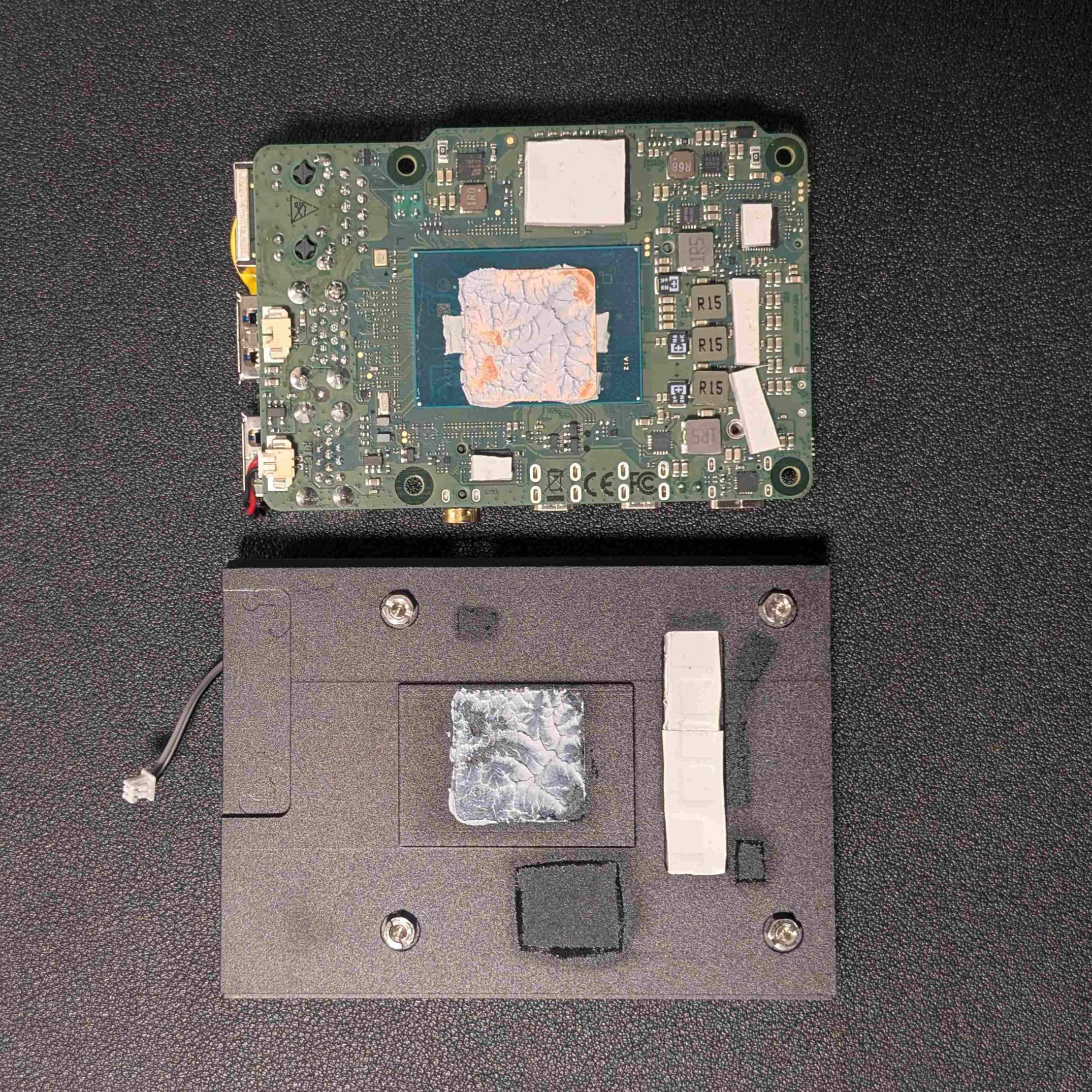
3. Radxa X4 Copper Shim Guide
This in an important mod to improve cooling efficiency involves using a 1mm copper shim paired with Arctic Cooling MX-6 thermal compound to create a better heat transfer interface between the exposed CPU and GPU cores and the cooling solution.
For those looking to replicate the performance-enhancing modifications on the Radxa X4, here are the exact components I used for under US$15 in total:
- 🛒 1mm Copper Shim for CPU Cooling – Buy on AliExpress
- 🛒 2230 NVMe Micro-Tower Heatsink – Buy on AliExpress
- 🛒 3dBi Wi-Fi Antenna Upgrade Kit – Buy on AliExpress
Step-by-Step instructions:
- Precision Alignment with a Thermal Pad “Frame”
- Given that the Intel N100’s CPU and GPU dies are exposed silicon, care must be taken to prevent tilting or misalignment, which could lead to cracks or uneven pressure distribution.
- A 1mm thermal pad “frame” was placed around the exposed cores, acting as a stand for the copper shim to ensure even contact and avoid stress fractures.
- Application of Arctic Cooling MX-6 Compound
- Between the exposed core and copper shim for efficient heat transfer.
- Between the copper shim and the Radxa stock heatsink to minimize thermal resistance.
- Additional Thermal Management Enhancements
- 2mm thermal pads were applied to heat-sensitive components, including the RAM modules, voltage regulators & MOSFETs.
- This improves long-term durability and ensures thermal stability under the increased 15W power envelope.
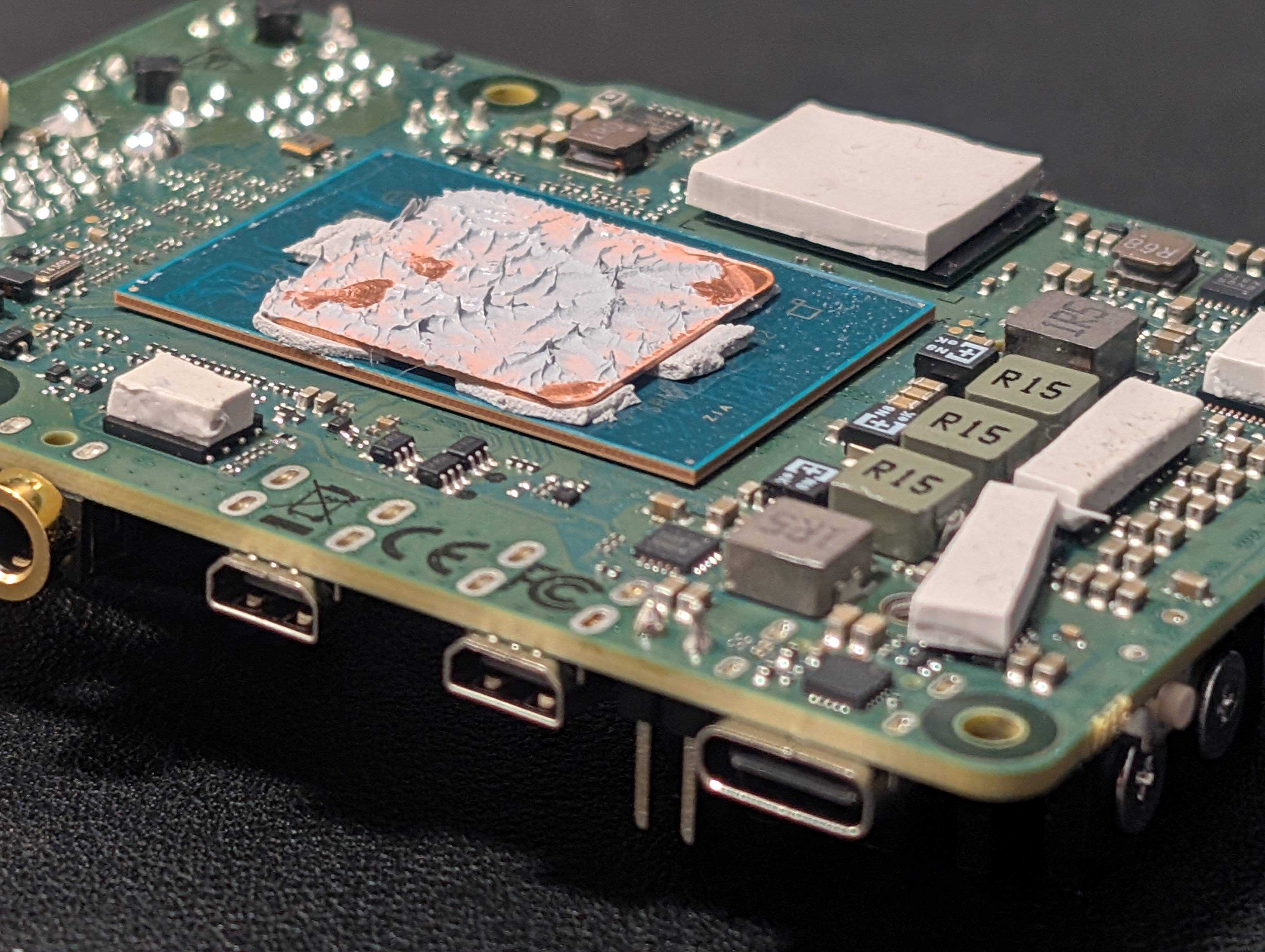
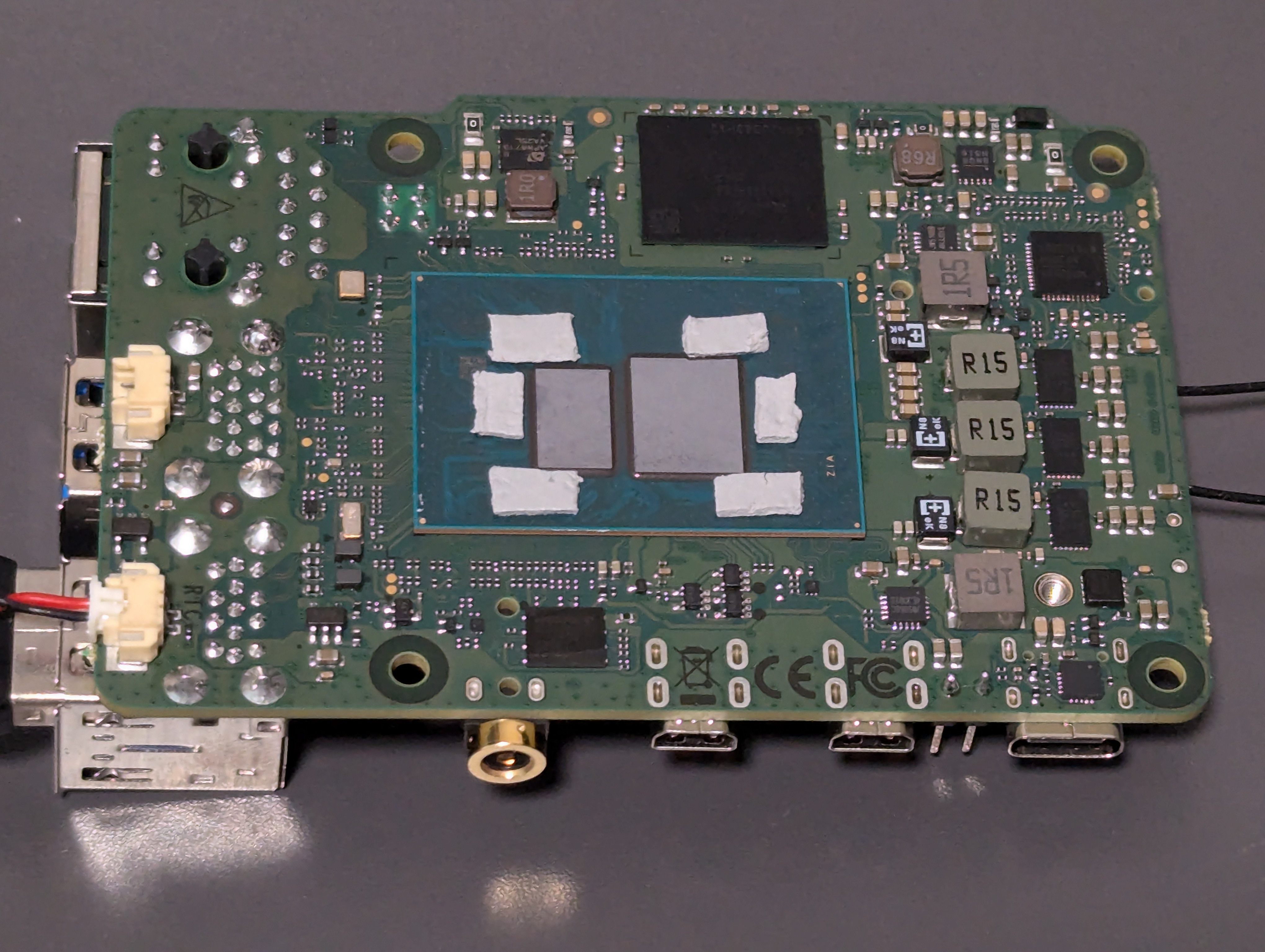

Note the 2mm thermal pads applied on the various heat generating chips (ram, MOSFETs, voltage regulators etc.)

4. Performance Gains: Lower Temperatures, No Throttling
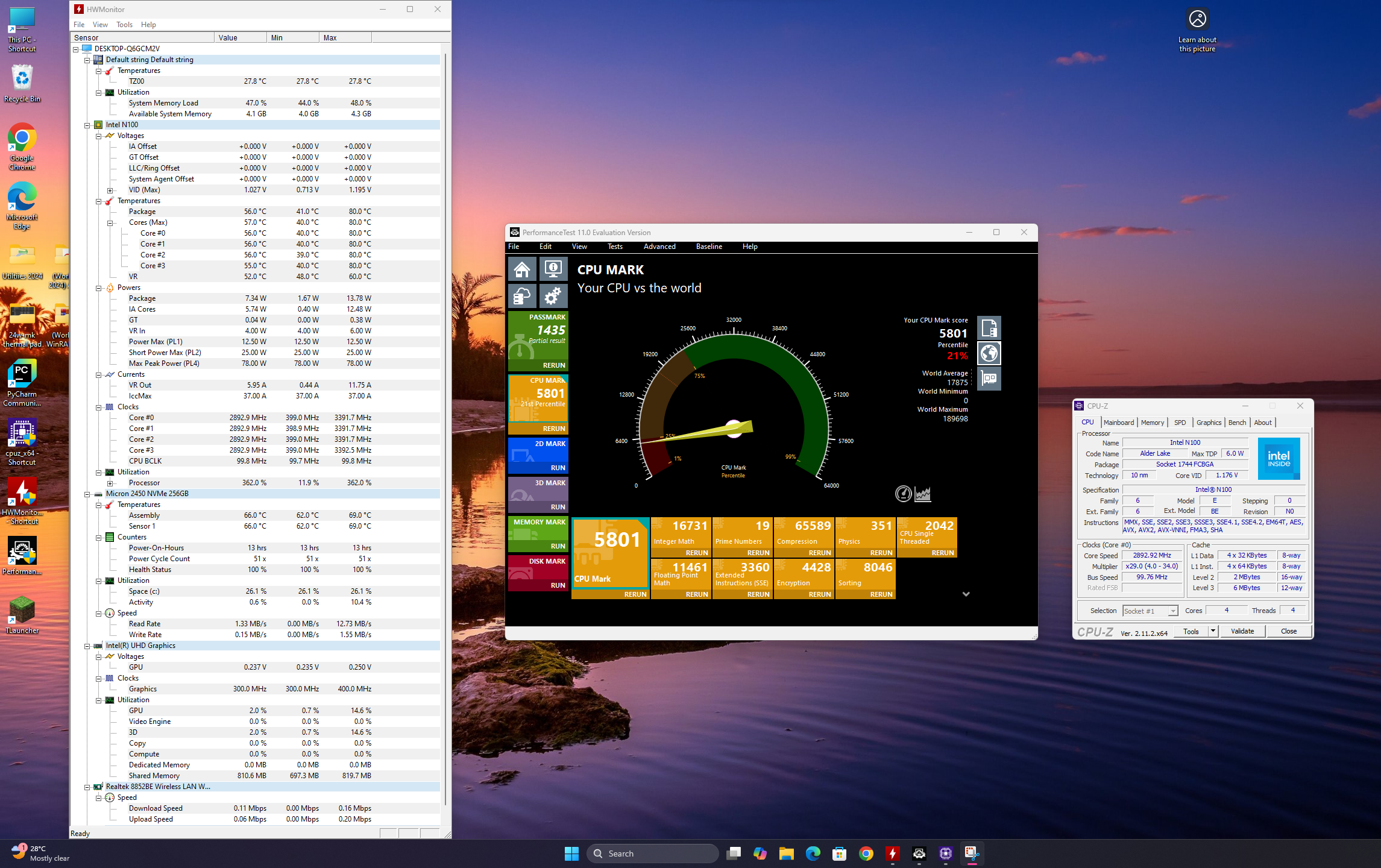
With the copper shim mod in place, benchmarking results under PassMark showed peak temperatures staying within 80°C—far from the 96-97°C throttling threshold observed in stock configurations. Under real-world workloads, including gaming and media playback, the system consistently ran at even lower temperatures.
A Minecraft instance running at 1440p saw CPU temperatures peak at 70-71°C, meaning that under practical applications, the Radxa X4 remains cool, stable, and free from throttling issues.
Why This Mod Matters on the Radxa X4
- Unleashes full N100 potential (15W envelope, 34x multiplier)
- Ensures stable performance under sustained loads
- Prevents throttling issues common in stock setups
- Extends longevity of board components
For users looking to maximize their Radxa X4 for serious computing applications, this cooling mod is highly recommended. Paired with NVMe storage and the built-in 128GB eMMC option, the X4 is truly a desktop-class SBC that far surpasses traditional ARM-based Raspberry Pi 5 setups.
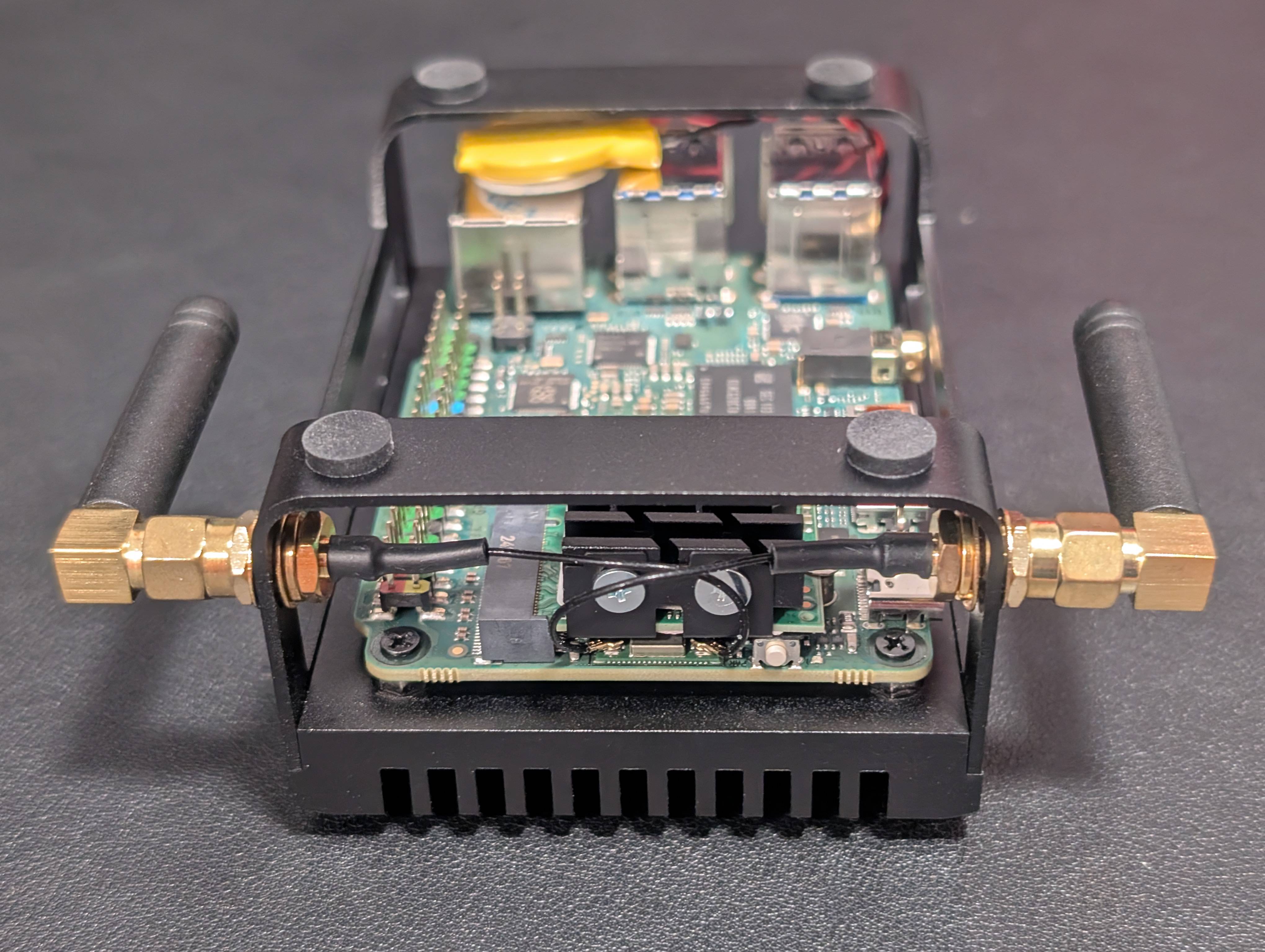
Radxa X4 Optional Mods: Maximizing Wireless Performance and Storage Cooling
Beyond the copper shim thermal mod, here are recommended optional modifications that significantly improve the Radxa X4’s wireless performance and NVMe thermals. These enhancements address the “flippy” stock Wi-Fi antennas and high NVMe temperatures due to the compact design.
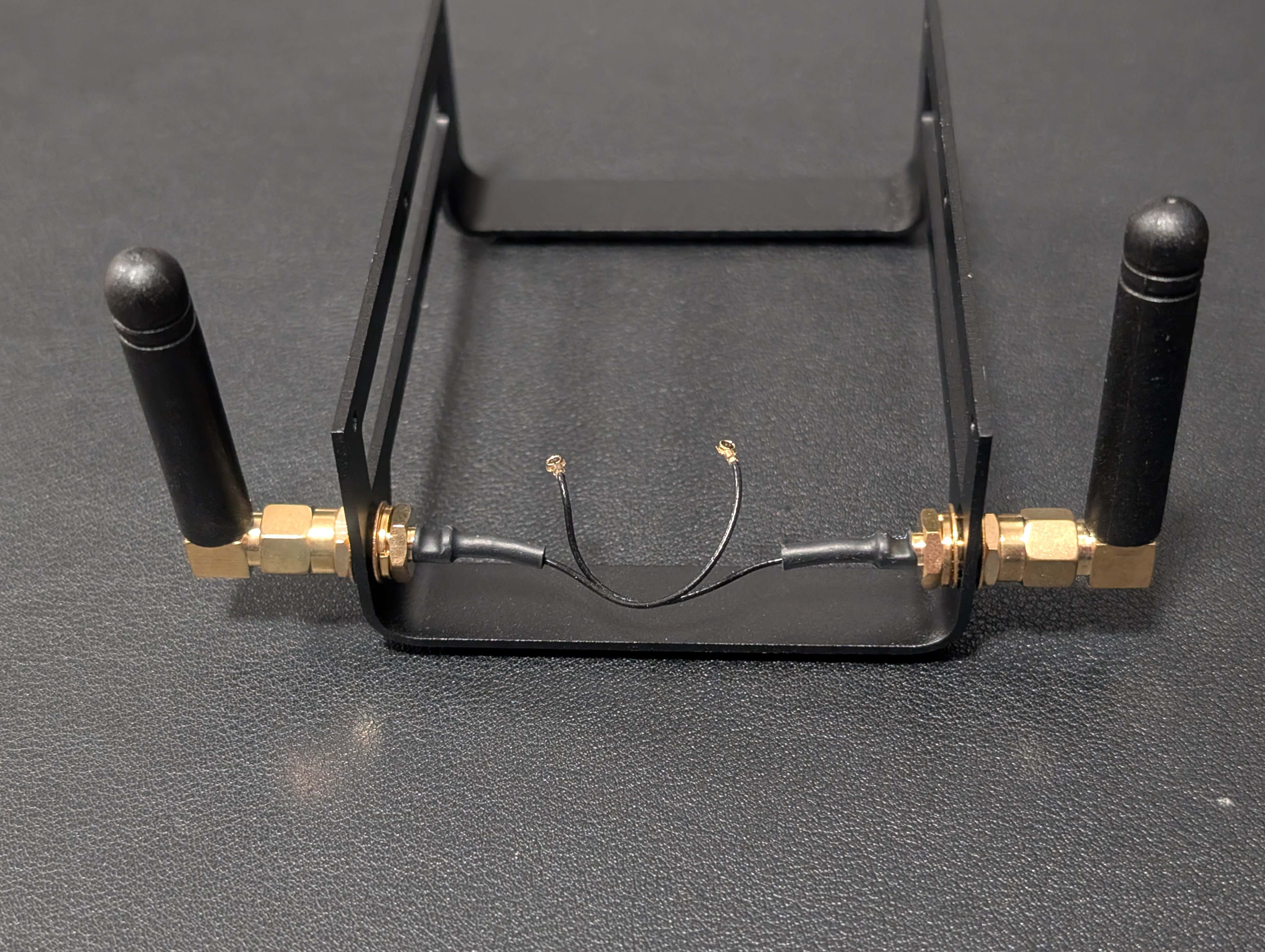
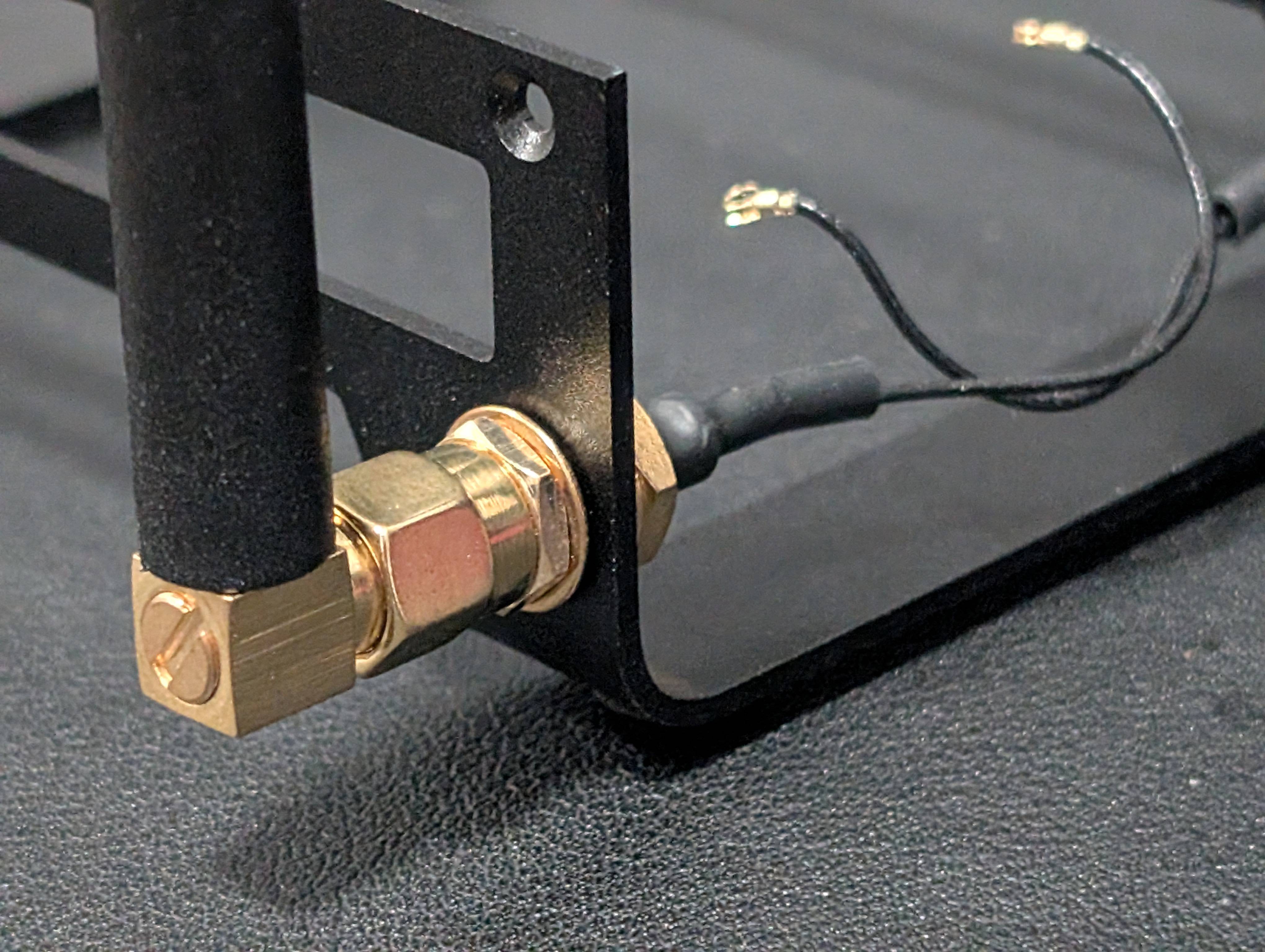
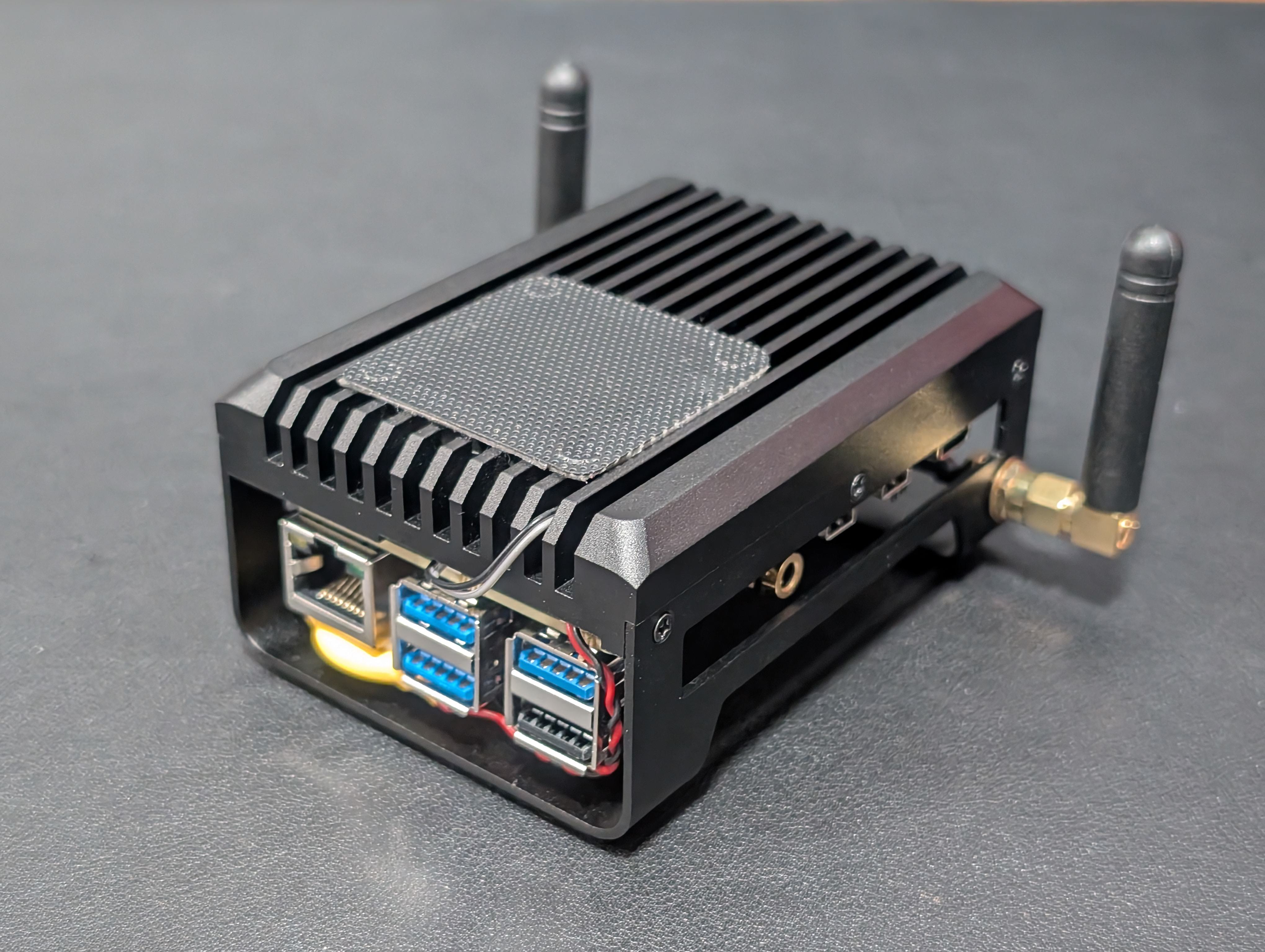
1. Upgrading Wi-Fi Antennas for Stronger & More Reliable Connectivity
While the Radxa X4 includes onboard Wi-Fi, it comes with flimsy, paper-thin “flippy” antennas, which can be a nuisance to deal with. The new revision of the Radxa X4 heatsink assembly frame comes with dedicated Wi-Fi antenna mounting holes, making it easier than ever to install higher-gain external antennas.
Recommended Upgrade:
- Swap out the stock antennas for 3dBi or 5dBi mounted Wi-Fi antennas for significantly better signal reception and transmission.
- This mod ensures more stable connectivity, especially when using the X4 in high-bandwidth applications like media streaming, cloud storage, or remote desktop access.
2. Managing NVMe Temperatures: Compact, Effective Cooling Solution
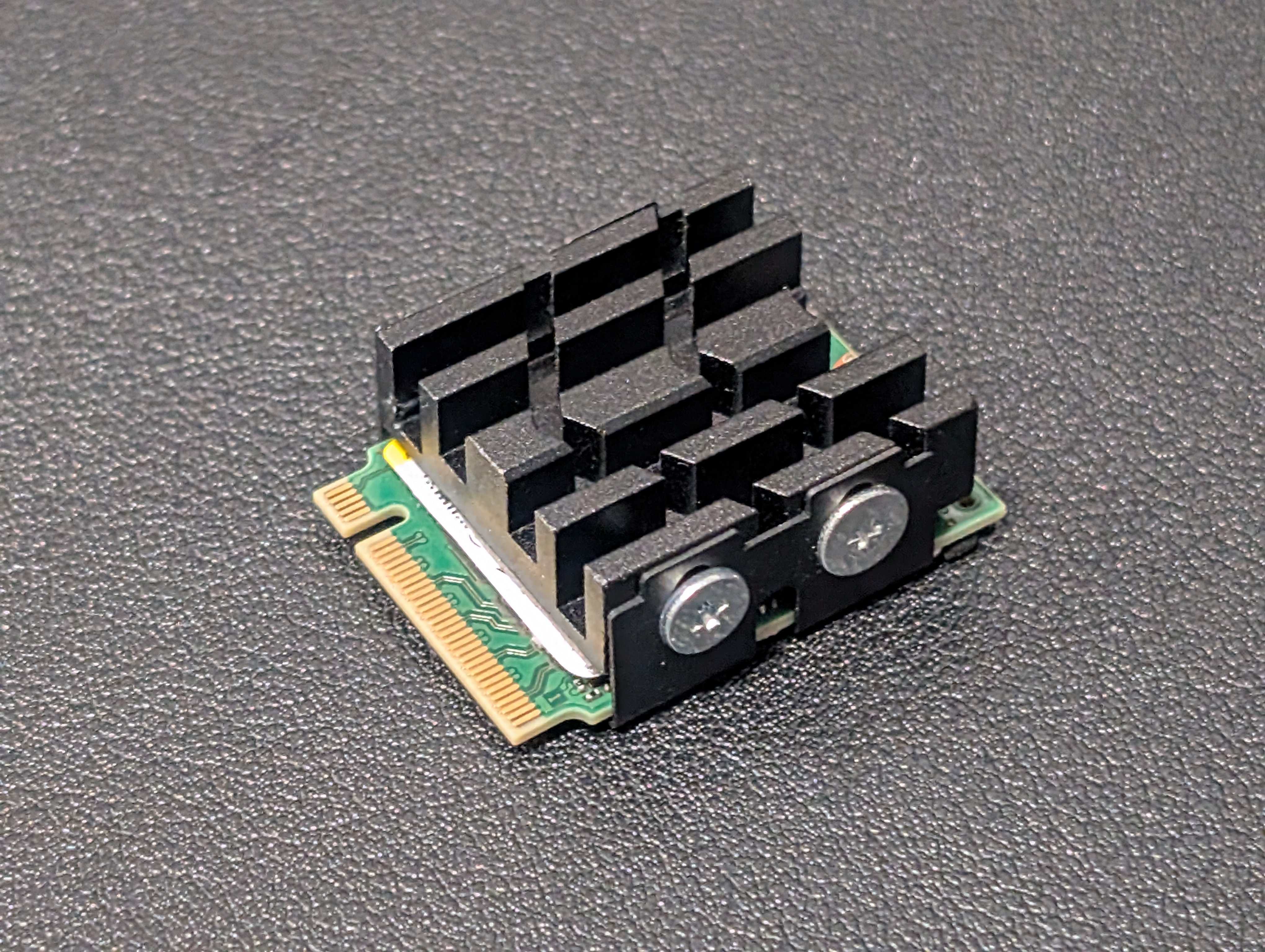
The Radxa X4 supports M.2 2230 NVMe SSDs, which run significantly hotter than traditional SATA storage. In my setup, I installed a Gen 4 Micron 2230 NVMe SSD, and under normal real-world usage, the drive was hitting 75-80°C consistently—potentially affecting both performance (throttling) and lifespan.
The Solution: A Micro-Tower Style NVMe Heatsink
To mitigate overheating while maintaining compatibility with the compact layout, I found a micro-tower style NVMe heatsink that:
- Effectively lowers SSD temps
- Fits neatly into the cramped space without interfering with other components
- Prevents thermal throttling during sustained operations
After installing the heatsink, NVMe temps dropped significantly, keeping the SSD within an optimal thermal range even under heavy usage.
These two auxiliary mods—Wi-Fi antenna upgrade and NVMe cooling solution—transform the Radxa X4 into a more stable, high-performance SBC. Combined with the copper shim mod for CPU cooling, this x86-based board stands out as a true desktop-class alternative to the Raspberry Pi 5, making it ideal for serious computing projects.
Radxa X4 Design Quirks: Lithium Battery Placement & Poor Bluetooth Connectivity
There are a few design quirks that users should be aware, which are the lack of a dedicated lithium battery mounting space and potential Bluetooth interference when using an NVMe heatsink.
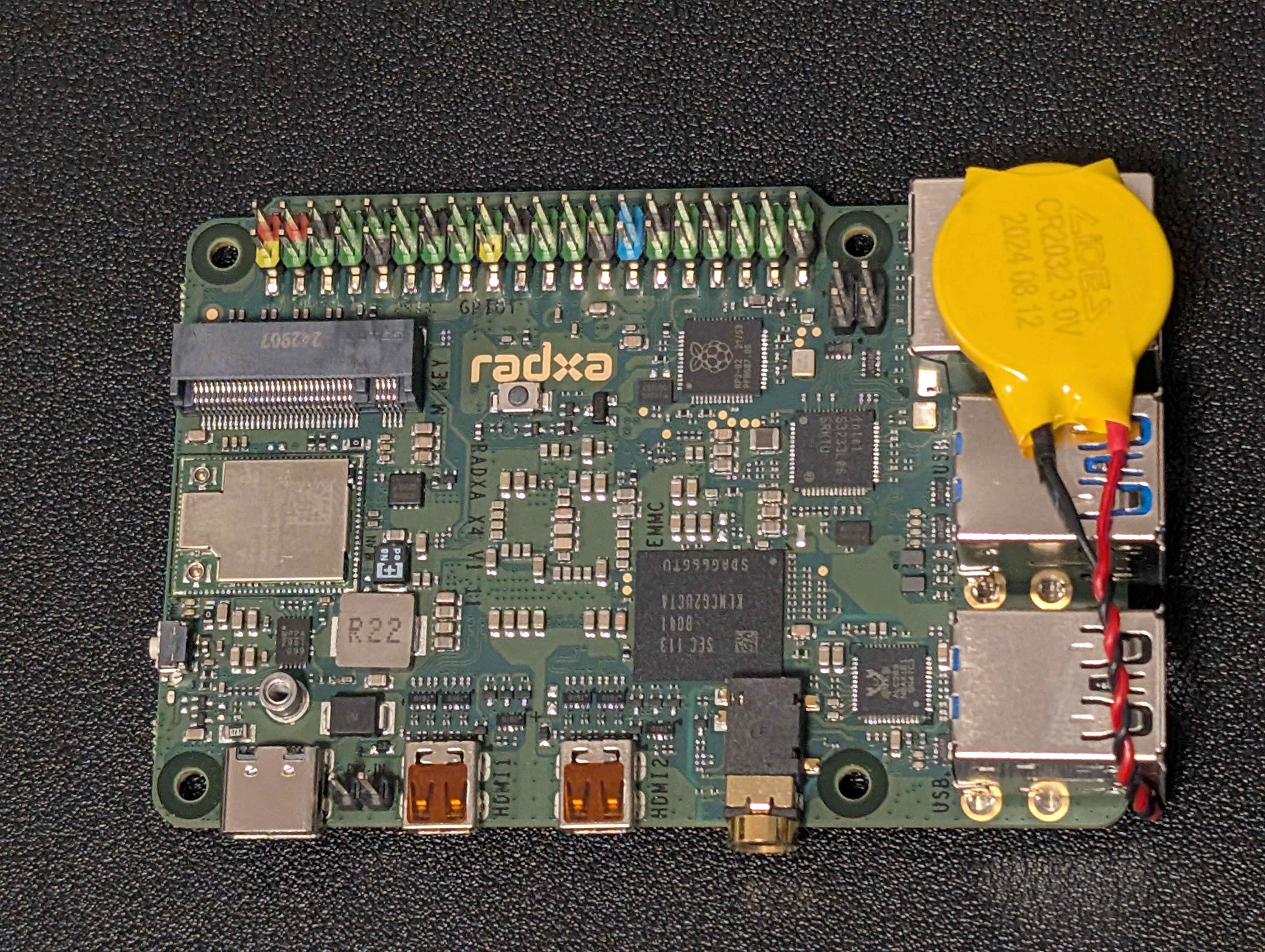
1. Lithium Battery Placement Issue: Nowhere to Securely Mount It
The inclusion of a lithium battery for RTC (Real-Time Clock) functionality is great, ensuring that the system maintains accurate time even when powered down. However, Radxa didn’t provide a dedicated mounting space for the battery, leaving users to figure out where to place it.
The Problem:
- With no dedicated slot, bracket, or adhesive mounting area, many users end up sticking the battery onto the I/O connectors or directly onto the board as a workaround.
- This isn’t ideal, as it blocks access to ports and may cause accidental disconnections during maintenance.
- Over time, heat exposure from surrounding components may degrade the battery’s longevity.
Possible Solutions:
- A 3D-printed battery holder could be a neat fix for securing the battery without interfering with components.
- Using a small adhesive-backed velcro strip might provide a temporary but adjustable mounting solution.
- Radxa should ideally address this in future revisions with a dedicated battery slot or mount.
2. Bluetooth Interference Issue: NVMe Heatsink Placement Matters
One unexpected issue arises when using a large NVMe heatsink—it can negatively impact Bluetooth connectivity due to its placement over the onboard Wi-Fi/Bluetooth module.
The Problem:
- The Wi-Fi/Bluetooth module is positioned directly under the SSD slot, meaning a large heatsink partially or fully blocks the module.
- This leads to degraded Bluetooth performance, resulting in weaker signals, connection dropouts, or lag when using Bluetooth peripherals like keyboards, mice, or headphones.
Recommended Fix:
- If you need stable Bluetooth connectivity, an external Bluetooth dongle is highly recommended.
- This bypasses the interference issue entirely, ensuring uninterrupted signal strength.
- Fortunately, any standard USB Bluetooth adapter works well with the Radxa X4.
While these quirks aren’t dealbreakers, they do require some creative solutions. The RTC battery placement issue is an annoyance that could be fixed with a simple bracket or 3D-printed holder, while the Bluetooth interference issue can be easily mitigated by using an external Bluetooth dongle.
Comparing the Radxa X4 to the Raspberry Pi5
| Feature | Radxa X4 | Raspberry Pi 5 |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Intel N100 (x86, Quad-Core, up to 3.4GHz) | Broadcom BCM2712 (ARM, Quad-Core, 2.4GHz) |
| Architecture | x86 (full desktop & enterprise software compatibility) | ARM (limited software compatibility) |
| Memory | 4GB, 8GB, 12GB, 16GB LPDDR5 | 4GB, 8GB, 16GB LPDDR4 |
| Storage | NVMe (M.2 M-Key) + eMMC (up to 128GB) | MicroSD (no native NVMe support) |
| Connectivity | 2.5 GbE, Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5 | 1 GbE, Wi-Fi 5, Bluetooth 5 |
| USB Ports | 3x USB 3.0, 1x USB 2.0 | 2x USB 3.0, 2x USB 2.0 |
| Display | 2x Micro HDMI (4K@60Hz) | 2x Micro HDMI (4K@60Hz) |
| GPIO | Raspberry Pi RP2040-controlled 40-pin | Native 40-pin GPIO |
| Cooling | Requires modifications for best performance | Requires add on cooler for best performance |
Final Thoughts: Is the Radxa X4 Worth It?
The Radxa X4 is not just another SBC—it is a serious desktop-class alternative that redefines what single-board computing can achieve. While the Raspberry Pi 5 is excellent for IoT, hobbyist, and small-scale projects, the Radxa X4 is a different beast entirely.

- For power users, its x86 architecture, superior storage, and high RAM options make it a true desktop replacement.
- For NAS builders, developers, and embedded system designers, the native NVMe, 2.5GbE, and eMMC storage simplify deployments.
- For those seeking raw computing power, BIOS and cooling mods can unleash performance levels unseen in other SBCs.
While the lack of Pi HAT compatibility may deter some users, the trade-off is access to a fully-fledged x86 platform, making it the most powerful and versatile SBC solution available today.
If you are a serious SBC user looking for an alternative to the Raspberry Pi with desktop-class capabilities, the Radxa X4 is your best bet.
Support My SBC Explorations on Patreon! 🚀
If you found this Radxa X4 review helpful and want to see more SBC reviews, mods, and in-depth explorations, consider supporting my work on Patreon!
🔗 Join the community & support my work here: patreon.com/NashRaj
Thank you for being part of this journey! 🙌🚀
